Diabetes mellitus (DM) from the Greek word diabaínein. That is translucent or "water fountain". And in Latin, mellitus, sweet flavor commonly known as diabetes.
It is a disease characterized by hyperglycemia (elevated blood sugar levels) continuous and varied, especially after eating.
Another source said that diabetes mellitus is a state of chronic hyperglycemia is accompanied by a variety of metabolic disorders due to hormonal disorders.
As a result of various chronic complications in the eyes, kidneys, and blood vessels, with lesions in the basal membrane in electron microscopy.
All types of diabetes mellitus have similar symptoms and complications at advanced levels. Hyperglycemia itself can lead to dehydration and ketoacidosis.
Long-term complications include cardiovascular disease (double the risk), chronic renal failure (the main cause of dialysis), retinal damage which can lead to blindness.
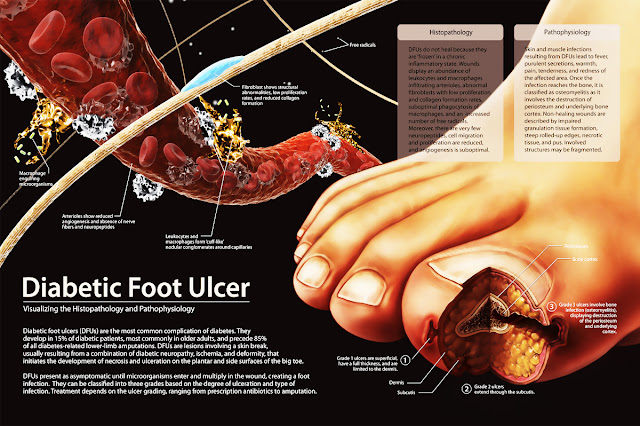
In addition to nerve damage that can cause impotence and gangrene with risk of amputation. More serious complications more common when poor control of blood sugar levels.
Formation of diabetes is important is due to insufficient production of insulin (type 1 diabetes mellitus, the first known), or lack of sensitivity of body tissues to insulin (type 2 diabetes, the more common form).
In addition, there are also types of diabetes mellitus caused by insulin resistance that occurs in pregnant women.
Type 1 requires insulin injections, while type 2 resolved with oral medication and only requires insulin if the medicine is not effective. Diabetes mellitus in pregnancy usually resolves itself after delivery.
Understanding and patient participation is vital as blood glucose levels change continuously, due to the success of keeping blood sugar within normal limits can prevent complications of diabetes.
Other factors that may reduce complications is to quit smoking, optimizing cholesterol levels, maintain a stable body weight, high blood pressure control, and regular exercise.
What is the Diabetes Mellitus?
Diabetes Mellitus or DM is one of the health issues that impact on productivity and can reduce human resources. This disease not only affects the individual, but the health system of a country.
Although there is no national survey, in line with lifestyle changes including diet Indonesian society expected people with diabetes is increasing, particularly in the age group up to the entire adult socio-economic status.
Currently diabetes disease prevention efforts have not occupy the main priorities in health care, although known to the resulting negative impact is quite large among other chronic complications in chronic heart disease, hypertension, brain, nervous system, heart, eyes and kidneys.
DM is a degenerative disease, where there is interference metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins and is characterized by high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia) and urine (glucosuria).
What causes of Diabetes Mellitus?
Diabetes mellitus or diabetes is a disease which is caused by the increase in blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia) due to insulin deficiency both absolute and relative.
Absolut means no insulin at all, while the relative mean it is quite a bit higher or power works or less, the hormone insulin made in the pancreas.
There are two types of Diabetes Mellitus:
Called Type I diabetes or insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. DM is caused due to deficiency of insulin in the blood that occurs due to destruction of pancreatic beta cells.
Prominent symptom is the occurrence of frequent urination (especially at night), often hungry, and often thirsty.
Most people with this type of diabetes normal weight or underweight. Usually occurs at a young age and require insulin for life.
Or so called type II DM independent of insulin. DM is due to the insulin that is there does not work properly, insulin levels may be normal, low or even increased, but the function of insulin for glucose metabolism no or less.
As a result, glucose remains in the blood causing hyperglycemia high, 75 percent of patients with type II diabetes or obesity there are very overweight and usually known DM after the age of 30 years.
Overweight or obesity is a risk factor for diabetes disease, in the treatment of diabetic patients, in addition to anti-diabetic drugs, needs to be supported with dietary therapy to lower blood sugar levels and prevent other complications.
What are the symptoms of people suffering from Diabetes Mellitus?
The typical clinical symptoms of diabetes mellitus are "triaspoli" polydipsia (drinking a lot), poliphagia (lots of eating) and polyuria (urinating a lot). In addition to the complaints often accompanied by tingling, especially in the fingers of the hand, the body feels weak, itching, and when there are difficult wounds healed.
Sometimes weight decreases dramatically. To determine whether a diabetes mellitus is by checking blood sugar levels. Normal blood sugar levels during fasting (nuchter) = 80 - <110 mg / dl and after eating = 110 - <160 g / dl.
Complication
If the blood sugar level is constantly high mean uncontrolled, over time there will be complications (complications) which basically occurs in all blood vessels.
For example, the blood vessels of the brain (stroke), blood vessels of the eyes (blindness can occur), renal vein (Chronic Renal Failure/CRF) or hemodialysis, and others.
If this has happened complicate the effort to heal the direction normal circumstances is very difficult.
Therefore, early prevention efforts for the required and expected complications is very useful to avoid things that are not profitable.
How to prevent and treat Diabetes Mellitus?
DM can be prevented by implementing a healthy lifestyle as early as possible is to maintain the daily diet is healthy and balanced by increasing the consumption of vegetables, fruit, and fiber. Besides limiting foods high in carbohydrates, protein, and fat.
Not only that, maintaining a normal body weight according to age and height as well as regular exercise according to age and ability is an effective means for prevention.
The goal of treatment is to reduce the diabetic patient symptoms, lowering the BB for obesity and prevent complications.
Tips to cope with diabetes mellitus
1. Diet
DM patients are strongly encouraged to diet as recommended, which will be treated antidiuretic or insulin. Must comply with the diet continuously both in the number of calories, the composition and meal times to be arranged. Obedience is very necessary also when the invitation or party, travel, sports, and other activities.
2. Medications
Antidiabetic tablets or injections are given, but the diet therapy should not be forgotten as well as other complications that accompany the medication or insulin injections.
3. Sports
With regular exercise, the sensitivity of cells to insulin for the better, so the insulin that although there is relatively less can be used more effectively. Do exercise 1-2 hours after meals especially morning for ½ to 1 hour per day at least 3 times a week.
People with diabetes should consult a doctor or nutritionis nutrition (nutritionist) every six months to adjust your diet and eating patterns to accommodate growth and changes in body weight according to the pattern of life.
Planning nutrition patients with Diabetes Mellitus:
1. Judgment of the condition of patients
Nutritional status: assessment of nutritional status by calculating the Body Mass Index (BMI) = weight (kilograms) or TB2 (meters) to see whether people with diabetes are overweight or obese, normal or malnourished. Normal BMI in adults between 18.5 to 25.
2. Tolerance glucose
By giving blood sugar (glucose) whether the tolerance limits of normal (control). Usually the fasting blood sugar checked and two hours after a meal, blood sugar and as HBAC. It also examined the levels of sugar in the urine.
3. Complications other
Clinical and laboratory examinations may be necessary if further to see if there is either acute or chronic complications such as blood sugar levels are always low or always high, complications to heart disease, kidney, liver, blood vessels, nerves or eyes.
4. Dietary planning and educating patients with DM
Aims to educate diabetic patients that patients can control blood sugar, reduce complications and improve the ability to care for themselves. Diet plan aims for sufficient intake of calories, protein, fat, mineral acids, fiber, and water.
With the frequency of meals throughout the day tailored to the anti-diabetic medication or insulin injections. Besides the calorie and other nutritional fiber adapted to the nutritional and health status of people with diabetes.
For example, when accompanied by hypertension or high blood pressure, had to follow a low-salt diet). Diet plan can use the exchange list food ingredients, so people with diabetes can use the list itself.
5. Sports
People with diabetes are encouraged to do regular exercise 3-4 times each week. At least 20-30 minutes, for example, fast walking or gymnastics. This is to improve insulin activity. Besides exercise helps weight loss fat or obese patients.
When doing strenuous exercise, preferably before, during and after exercise should monitor blood sugar levels, especially for diabetes mellitus type I. This is in order to determine the need for insulin and food intake should be adjusted.
When doing light exercise, no need to regulate insulin requirements, quite a small snack before exercise on blood sugar <80 mg / dl. To exercise longer, snack takes every ½ to 1 hour.
In a long and strenuous exercise such as cross-country skiing, mountain biking, etc, insulin dose needs to be reduced to prevent hypoglycemia (drop in blood sugar levels). In people with diabetes are encouraged to reproduce fluids before, during, and after exercise to prevent dehydration.
What harm diabetic patients?
DM disease can cause a variety of life threatening complications and affect a person's quality of life.
1. Complications of acute
The most dangerous complication is acute hypoglycemia (very low blood sugar levels), because it can lead to coma (unconsciousness) and even death if not quickly rescued.
The state of hypoglycemia is usually triggered because patients do not comply with the schedule of food (diet) that has been set. While people continue to take insulin antidiabetika or get an infection.
The symptoms of hypoglycemia are hunger, weakness, trembling, headache, cold sweats and even seizures.
2. Comma
In patients with diabetes mellitus can also be caused due to high blood sugar levels, which is usually triggered by the presence of disease or infection due to diabetic patients not taking medication or getting the recommended dosage of insulin.
The symptoms of hyperglycemia are thirst, warm and dry skin, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, dizziness and polyuria. Because it is difficult to distinguish complications due to hypo or hyperglycemia, it is recommended if there are symptoms such as the above in DM patients better be helped with water given sugar or candy, then the patient is immediately sent to the nearest hospital.
3. Complications of chronic
If it happens complication resulting in high blood sugar levels for a long time, such as disorders of the nerves, eyes, liver, heart, blood vessels and kidneys, in addition to efforts to lower blood sugar levels with insulin and antibiotic drug or dietary therapy, requiring treatment for complications.
Diet is also intended to reduce or cure these complications. For example, high cholesterol levels, then diet is directed also to lower the cholesterol levels.
What does nutrition with Diabetes Mellitus?
DM is a disorder of carbohydrate metabolism which is one element of the macro nutrients. This metabolic disorder also causes metabolic disorders other nutrients: proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals which the body's metabolic processes interact antarsemua nutrient elements.
Therefore, DM is one of the "Nutrition Related Disease" in which one of the disorders of metabolism of nutrients can cause disease. Diet therapy is the most important nutritional management in patients with DM.
Without setting the schedule and amount of food and quality of food throughout the day, it is difficult to control blood sugar levels to remain within normal limits.
If left for a long time, will lead to complications, either acute or chronic, which ultimately compromise the safety of patients with DM alone and affects work productivity.
For example, in patients with diabetes who were injured had to be amputated because of gangrene are always high in sugar so that the wound can not be healed.
What are the benefits of nutritional consultation?
Clinical nutrition provide nutritional counseling services for patients in need of therapy diet including diabetic patient. Here, people with diabetes are invited to get to know himself and is able to choose his food menu as needed.
Cover
DM disease medically incurable, but with willpower this disease can be controlled with a sufficient stock of knowledge and a strong desire. DM is not a disease so daunting.
But the methods of al hijamah or Oxidant Releasing Therapy or bruise, DM disease can be treated effectively and efficiently without the need for supplements and medicines.
From our experience since doing research and development Oxidant Releasing Therapy began in 2000 to patients with Diabetes Mellitus, Alhamdulillah many patients were successfully cured permanently (tested and proven in clinical trials).
To that end, rest assured and believe that God will not violate His promises. This means that if we are sick, it is He who has become a healer. Allah almighty knows best. (Candra P. Pusponegoro/various sources)